History
Since 2003, there are two main microprocessor design
- General purpose multicore CPUs
- many-thread GPUs.
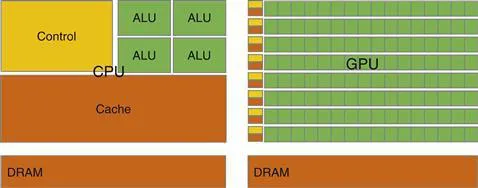
Difference
CPUs It makes use of control logic to allow instructions from a single thread to execute in and out of their sequential order while keeping the view of its sequential execution. General-purpose multicore CPUs typically have six to eight processor cores and on-chip cache memories. Limited by the memory bandwidth — rate at which data can be retrieved from memory. Has the large cache memory, low-latency arithmetic units. Has a latency-oriented design. GPUs shaped by the video game industry that pushes for performance of floating-point calculations per video frame(FLOPS). Large chip area while optimizing for power usage. Optimized to mazimize execution throughput of numerous threads while allowing each thread much longer execution time . This is known as throughput-oriented design. Factors in the choice of processors
- Large Consumer base(Installed base) — CUDA.
- Practicality and easy accessibility
- Support for IEEE floating standards.
2007- release of CUDA. Facilitate the ease of parallel programming.
Architecture of a Modern GPU
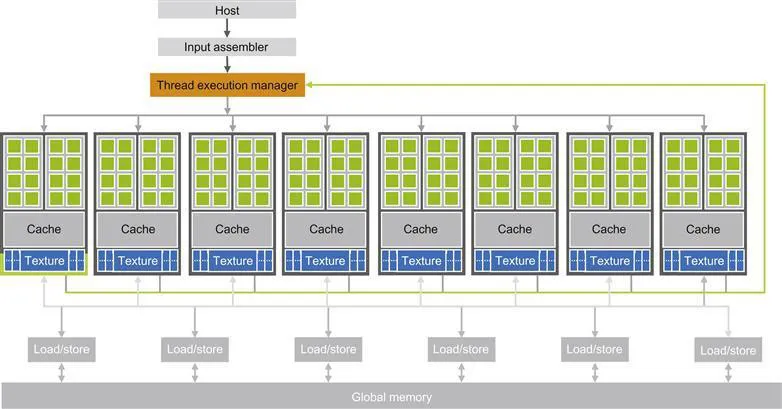
-
[Mattson2004] - proposed programming models
-
MPI2009 - MPI model for scalable cluster computing
-
Open2005 - OpenMP for shared-memort multiprocessor systems originally designed for CPU arch. consists of a compiler and runtime. An alternative is OpenACC supports multiple computers.
-
Khronos2009 - Open Compute Language(OpenCL), an alternative to CUDA, similar to CUDA, openCL programming model defines language extensions and runtime APIs for parallelism and data delivery manangement.
TODO
-
Computer Architecture
-
Parallel programming
-
Scalability across hardware
-
[[History of GPU computing]]
-
Cuda C/ heterogeneous CPU-GPU joint computing/SPMD
-
Floating points, precision, numerical stability
-
Parallel computation patterns
- Convolution
- Prefix sum/scan
- Sparse Matrix Computation
-
Case Study
-
OpenCL
-
OpenACC
-
Thrust
-
CUDA FORTRAN
-
C++AMP
-
MPI-CUDA
-
Dynamic Parallelism
DMA Modern computer systems use a specialized hardware mechanism called direct memory access (DMA) to transfer data between an I/O device and the system DRAM
An advantage of using a specialized hardware mechanism is that is designed for the primarily to copy data. DMA is used in data copy operations between a CPU and a GPU.
Fixed-function Graphics Pipeline
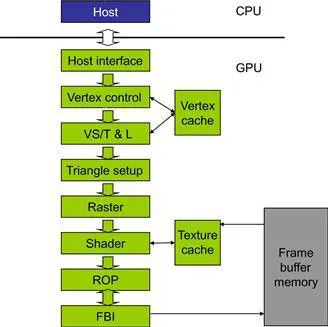 The NVIDIA Geforce Graphics Pipeline is designed to render triangles
The NVIDIA Geforce Graphics Pipeline is designed to render triangles
Steps
- CPU transfers Data with the help of DMA to GPU and vice-versa. This requires pinned memory in DRAM
- the vertex control records the vertices of the triangles and stores it hn a vertex cache for future use.
- the Vertex shading, transform and lighting (VS/T & L) stage transforms vertex and assign color, normals, texture coordinates ,tangents, …
- Raster stage assigns pixels to each triangles per vertex value.
- the shader stage assigns color through a combination of interpolation of vertex colors, texture mapping, per-pixel lighting mathematics, reflections, and more.
- Finally a raster operation (ROP) performs color raster operation and also determines visible vertices from occluded ones.
- Frame Buffer Interface (FBI) mamges memory read and write to display buffer memory.
Programmable processors came to life due to the increasing sophistication of software demands.
- In 2001, the NVIDIA GeForce 3 introduce shader programmability