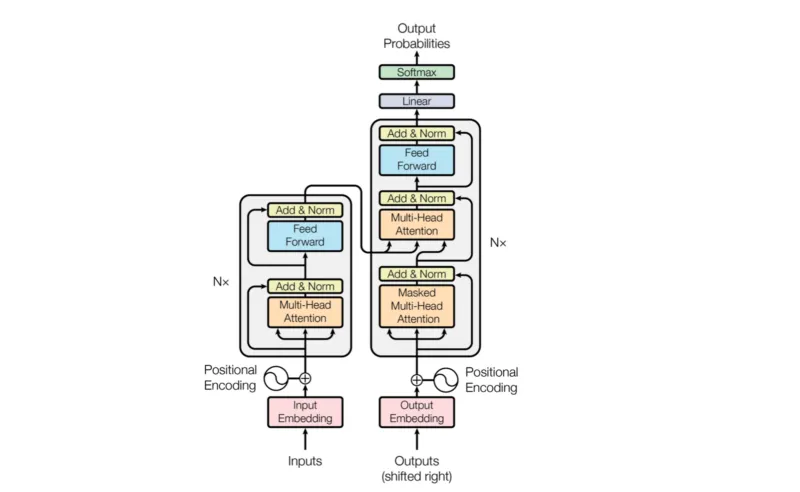
The transformer model is by far the most notable deep learning architecture till date. It is well-known for its use in LLMs and diffusion models. It was developed by Google, first proposed in the paper Attention is all you need.
One key innovations of the Transformer model is its ability to parallelize computation across sequence elements, making it efficient for training on large datasets. This parallelization, coupled with the absence of recurrent connections, allows the Transformer to achieve impressive performance in various NLP tasks, while mitigating the challenges associated with vanishing and exploding gradients.
The reason of the Transformer’s acclaim was its departure from the traditional sequential processing paradigms. such as RNNs and CNNs. Unlike RNNs, which processes input sequences sequentially and CNNs which operate on a moving fixed-sized window, the transformer relied on self-attention Mechanisms.
First of all, a text corpus is chosen such as Wikipeidia Corpus or Common Crawl, the text is then converted to numerical representations. The most notable tokenization methods, are SentencePiece and BPE. BPE is known for its use in compression algorithms. These tokens are then converted to a vector via a lookup table usually known as the Token Embedding/Word embedding. However, the transformer model does not only rely on the value,but as well as the position, So it depends on the combination of a token embedding and a positional embedding which captures the position of a token within a sequence length / context window. It is passed into a multi-headed attention. Attention is a vector of the interdependence of the tokens with one another.
Self-attention or intra-attention, enables the model to weigh the importance of different words in a sentence when predicting or generating the next word in a sequence. This attention mechanism allows the transformer to capture dependencies between words regardless of their positions, thereby alleviating the limitations posed by sequential processing and enabling parallelization across sequence elements.
Self-attention has no notion of position. It is just a weight of word dependencies. So, positions, similar to tokens is derived from an embedding table after the sum of both the token embedding and the positional embedding is fed into the attention block. Through this, the Transformer, not only can tell the next token but also the position along the sequence.
After attention is applied, it passes into a simple Multi-Layer Perceptron, to account for non-linearities and to reduce the channel size. Also, residual networks and normalization are applied, a de facto in reducing exploding and vanishing gradients.
This is basically all the decoder transformer architecture is all about.